Business Process Modeling (BPM) is a process representation technique that aims to understand, communicate, and optimize processes within organizations. It’s a high level of detail modeling that includes the activities to be performed, the people responsible for these activities, and the communication relationship between these people within the business, as we can see in the example of figure 1.
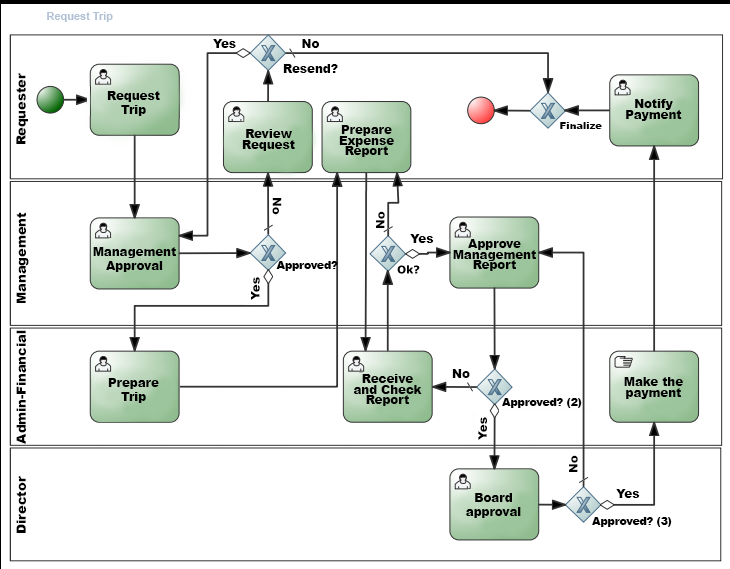
Figure 1: Example of business process modeling.
Approaching the business area is a challenge for computer scientists because it involves aspects such as: business scope definition and scope analysis. The business scope definition consists of abstracting what will be modeled and determining if this scope meets the client’s needs.
During the construction of the scope, it’s necessary that some questions are covered, such as:
- Who is the process customer?
- Does its scope meet the customer’s needs and aspirations?
- Which communication areas are involved in the process?
- What are the activity inputs and outputs?
- What are the key indicators, and how will they be measured in relation to deadlines and costs?
Process modeling is a link that helps in the understanding of the business that’ll be built along with information technology professionals. To facilitate the understanding of business process modeling it’s necessary to understand how the modeling life cycle works.
Business Process Modeling Life Cycle
As shown in figure 2, the cycle encompasses: design and analysis, configuration, execution, and evaluation.
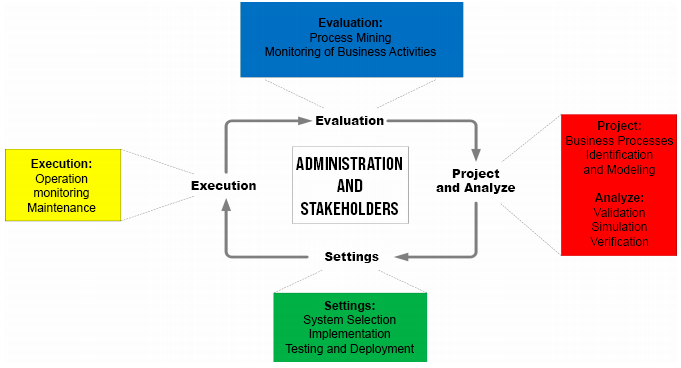
Figure 2: BPM Life Cycle.
Design and analysis consist of a survey about the processes, as well as the organizational and technical environment. The configuration is the inputs that allow modeling this process. Execution is related to monitoring and recording the steps of the flow to visualize the state of the process. Evaluation is an analysis of how this process is performing at its current stage, as well as what can be done to improve its productivity and meet the aspirations of involved stakeholders.
Basic principles of business process modeling
In addition to the life cycle concept, it’s important for us to understand the 9 basic principles of business process modeling. They are:
- Interaction between customer and organization
- Added value for the customer
- Decreased flow delays during activity exchanges
- Avoiding over-automation
- Standardize business processes
- Predict business rules
- Enforce compliance standards
- Validating BPM modeling
- Simplicity in process design
1. Customer-organization interaction
The interaction between the customer and a given organization is the key moment in a work that aims at modeling a process to improve the company’s productivity. During this interaction, the customer must feel that his company’s needs will be met in terms of cost, time, and money reduction.
This interaction is also known as the moment of truth because it establishes the initial trust relationship about who offers and who acquires the service.
2. Value added to the client
From the moment a relationship of trust is established with the customer, it’s necessary to perform a process modeling that adds value to his business, that is, if the activities of the process flow do not improve the productivity of the organizational sphere, it must be remodeled or a new flow must be performed.
3. Decreased flow delays during activity exchanges
During this process of redesigning and building a new flow it’s important to anticipate as much as possible the errors that can occur during the exchange of responsibilities in workflow activities so that delays do not occur.
4. Avoid over-automation
Another important factor is to avoid over-automation of processes. Therefore, it’s important to take five aspects into consideration when building the flow:
- Have a clear objective;
- Be careful not to detail the process too much;
- Take care not to under-detail the process;
- Review the model;
- Validate the model with stakeholders
5. Standardize business processes
Standardization in process modeling is important because a company often has several processes in its organizational hierarchy that are interconnected. Thus, when standardization occurs, it facilitates the operation of activities, increases productivity, improves quality, and reduces operating costs.
6. Predict business rules
Organizations also have specific business rules that determine the course of their operations and processes during execution and decision-making during business process activities.
7. Enforce compliance standards
Companies may have compliance standards that need to be taken into account when modeling the process, such as internal auditing standards. So it is always important to check if there are any rules that are intended for a particular type of organization.
8. Validation of the BPM modeling
The validation of the business model with the people involved in the process execution is fundamental because people may not be familiar with the process notations.
For this reason it’s recommended to perform an initial prototyping of the process, taking into consideration some good practices such as: includeing the essential fields; performing the simple configuration of the responsibilities streaks; creating manual tasks to represent the process activities, and also performing meetings with someone involved to conduct the interactions with the customer and another person to perform the validation and adjustments on the prototyping.
9. Simplicity in process design
This prototyping should be as simple as possible with the necessary information to make the process executable and satisfy the customer’s process improvement needs.
In conclusion
Business process modeling, allied to its construction principles, contributes to improving the organization’s communication during the activities that are performed, as well as automating and improving the companies’ process management, reducing the cost and time during the execution of the activities.
Want to learn more? Read our article What are the 5 most commonly used types of process mapping?