Process mapping is a methodology used to identify and sequence the steps of a process, its activities, inputs, and outputs in a structured way with the objective of seeking improvements and optimizations.
When the methodology is applied, the following benefits are clearly visible:
- Quality and increased customer satisfaction;
- Communication between departments;
- Productivity and cost reduction;
- Increased visibility of performance;
- Assertive and precise indicators.
In this article, read about the 5 most commonly used types of process mapping:
- Flowchart
- Horizontal flowchart
- Mapofluxogram
- UML – Unified Modeling Language
- BPMN – Business Process Model and Notation
1. Flowchart
Flowchart is the representation of the process through standardized graphic shapes and symbols that when sequenced form the drawing of the flow of a process. It aims to facilitate the understanding of the process through visual information, facilitating its analysis of improvements and optimization.
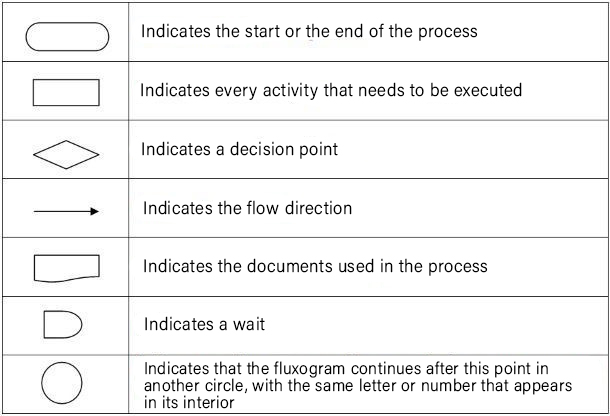
A strong feature of the flowchart is the use of symbols to represent the activities and steps in the process. In this image, we see what each symbol represents in a flowchart.
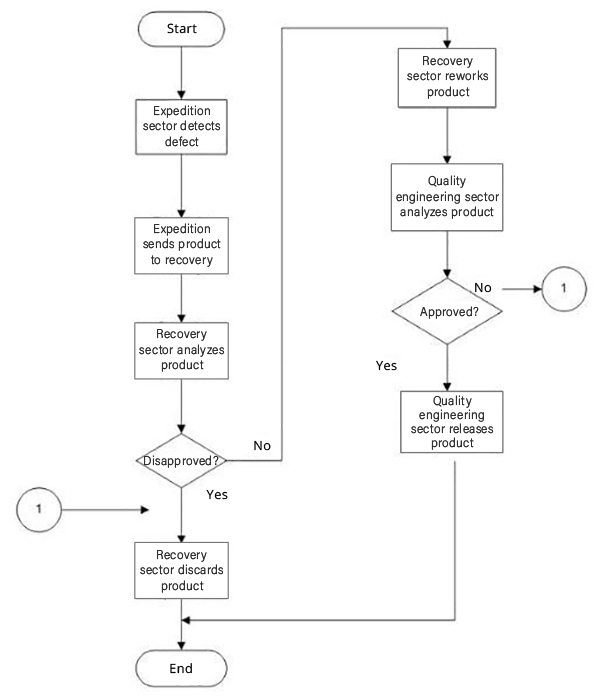
See also an example of a flowchart of a nonconforming product control process:
2. Horizontal flowchart
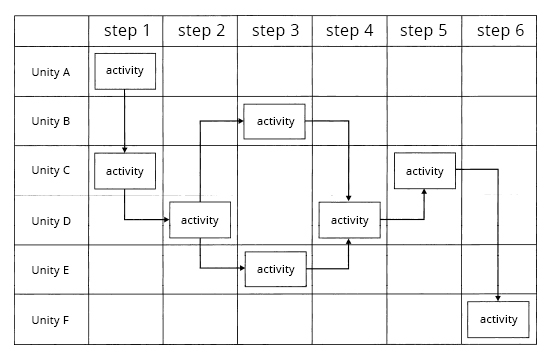
The horizontal flowchart is a more advanced and complete version of the flowchart. In it you can add more details to the process steps. The horizontal flowchart uses a matrix:
- The process steps are indicated on the horizontal axis and
- Those responsible for carrying out the activity are indicated on the vertical axis.
The image below depicts a representation of a horizontal flowchart with its units, steps and activities:
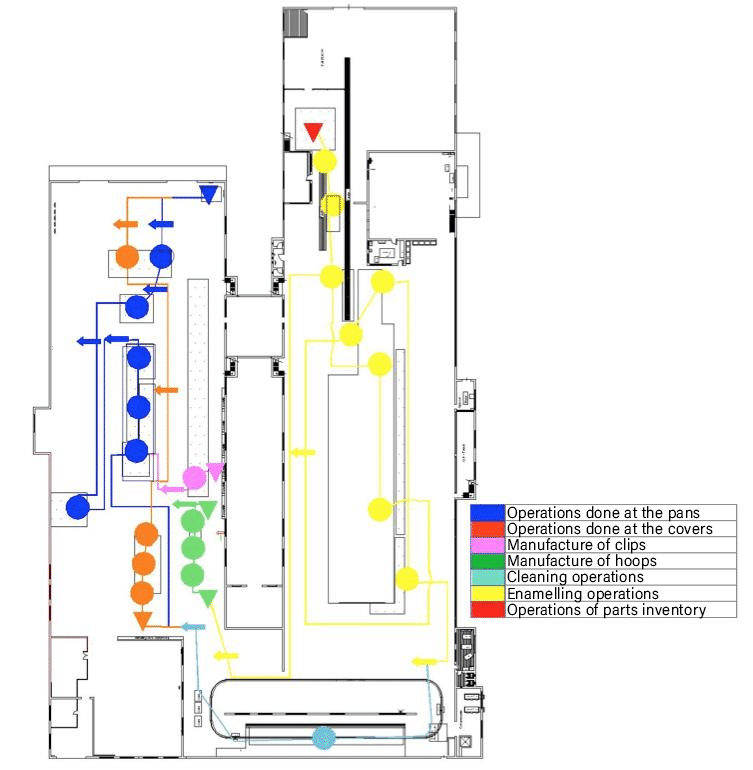
3. Mapofluxogram
The mapofluxogram is represented through a layout of the production line of a factory that shows the path of a product, material, form or person in a production line. It is like the union of the flowchart that we saw earlier, with the layout of the production line.
The following image shows an example of a mapofluxogram in a pan manufacturing process.
4. UML – Unified Modeling Language
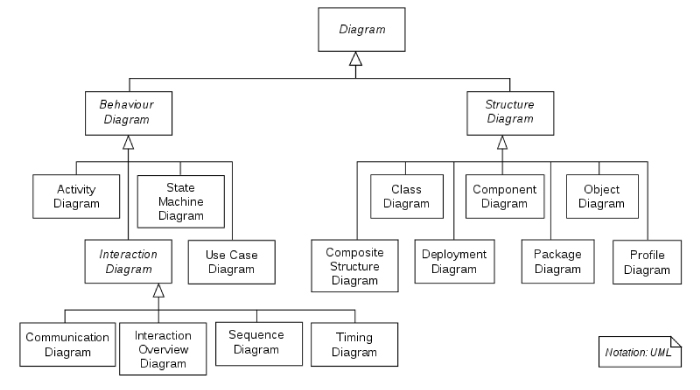
UML is the standardization of a set of diagrams with the main objective of structuring and describing any type of system, starting from the principle of diagrams. By applying UML to process modeling we can track the development of the process over time.
In UML version 2.2 there are fourteen types of diagrams divided into two categories: structural diagrams and behavioral diagrams:
- Structural diagrams are used to visualize, specify, construct and document the static aspects of a system.
- Behavioral diagrams are used to represent the structures of business classes, interfaces, control classes, and other systems.
The image below shows the structure of UML diagrams:
5. BPMN – Business Process Model and Notation
In the past professionals worked with different notations and different process modeling tools (some of which we have seen throughout this article). Over time this started to become unproductive for companies, users, and customers. With these difficulties arising, ideas emerged to standardize the language of business process modeling and so BPMN was born.
But after all, what is BMPN?
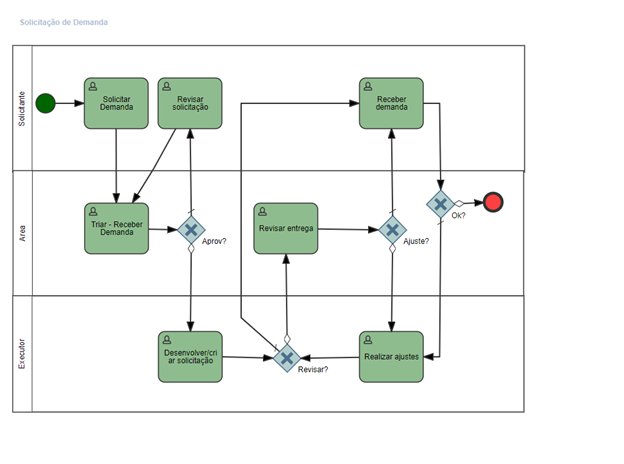
Briefly, BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation) is a notation created to standardize business process modeling. It is a notation that illustrates modeling in a simpler, more complete and precise manner.
As with flowcharts, BPMN also uses a standard symbology for its diagram. According to the BPM CBOK version 3.0, “symbols describe definite relationships such as workflow and order of precedence”.
The BPMN symbology consists of four groups:
- Swimlanes: are elements used to group tasks of a process that are performed by an actor.
- Artifacts: are used to provide additional text information about the process.
- Flow objects: these are the symbols of the activities, events, inputs, and outputs of the process.
- Connecting objects: these are the lines that connect the activities and components of the flow.
The image below exemplifies a BPMN diagram of a demand request process developed in the Fusion tool.
Conclusion
Regardless of which type of process mapping your company chooses to use, there needs to be strategic process management so that your organization can develop well-structured, systematized, and perfectly functioning processes.
The lack of process management in a company can be detrimental to business, especially when there is no standard or control of tasks. Inevitably there will be communication failures between departments, resulting in numerous damages to the corporation and employees.
To avoid these damages generated by the lack of quality and information management, it is recommended to use BPMN tools, such as the Fusion Platform tool. With the Fusion tool it is possible to automate your processes ensuring quality management and, consequently, resulting in the success of your business.
Still don’t know Fusion Platform? Try it for free for 15 days.